In the world of technologies, we often find new applications that offer some outstanding features and products. The technological world is constantly evolving at a staggering rate. Companies and firms focus on innovations to bring products into the market that can sell as utility, entertainment, and productivity.
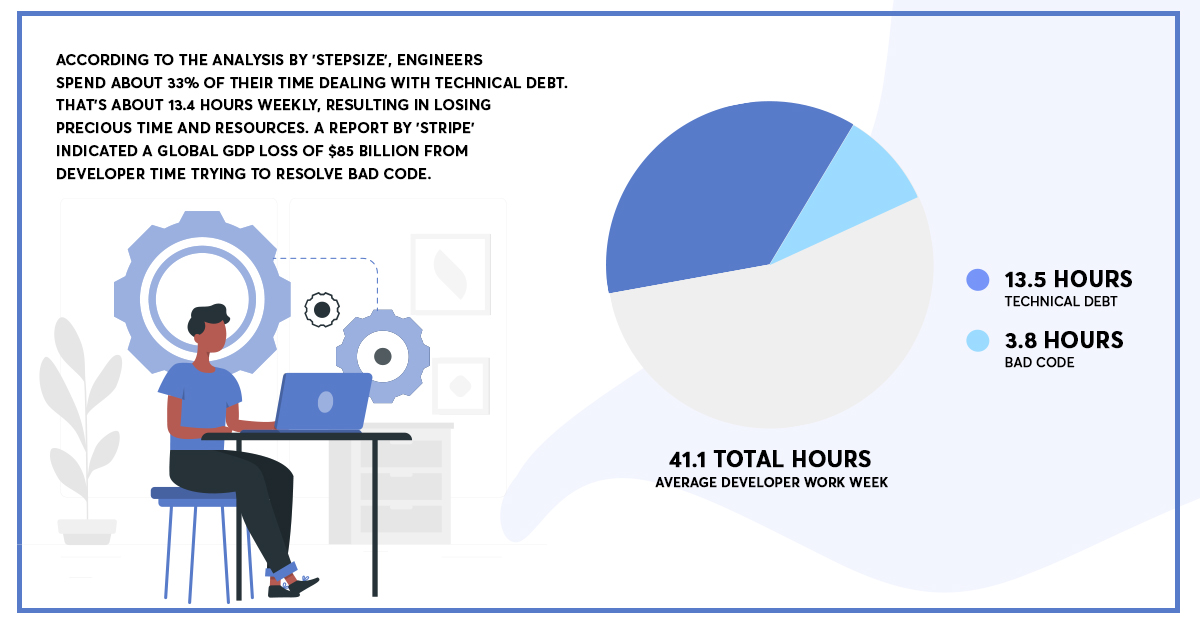 The flourishing demand and evolution of software applications and products lead to subtle problems in the technology world known as ‘technical debt.’ According to the analysis by ‘Stepsize’, engineers spend about 33% of their time dealing with technical debt. That’s about 13.5 hours weekly, resulting in losing precious time and resources. A report by ‘Stripe’ indicated a global GDP loss of $85 billion from developer time trying to resolve bad code.
The flourishing demand and evolution of software applications and products lead to subtle problems in the technology world known as ‘technical debt.’ According to the analysis by ‘Stepsize’, engineers spend about 33% of their time dealing with technical debt. That’s about 13.5 hours weekly, resulting in losing precious time and resources. A report by ‘Stripe’ indicated a global GDP loss of $85 billion from developer time trying to resolve bad code.
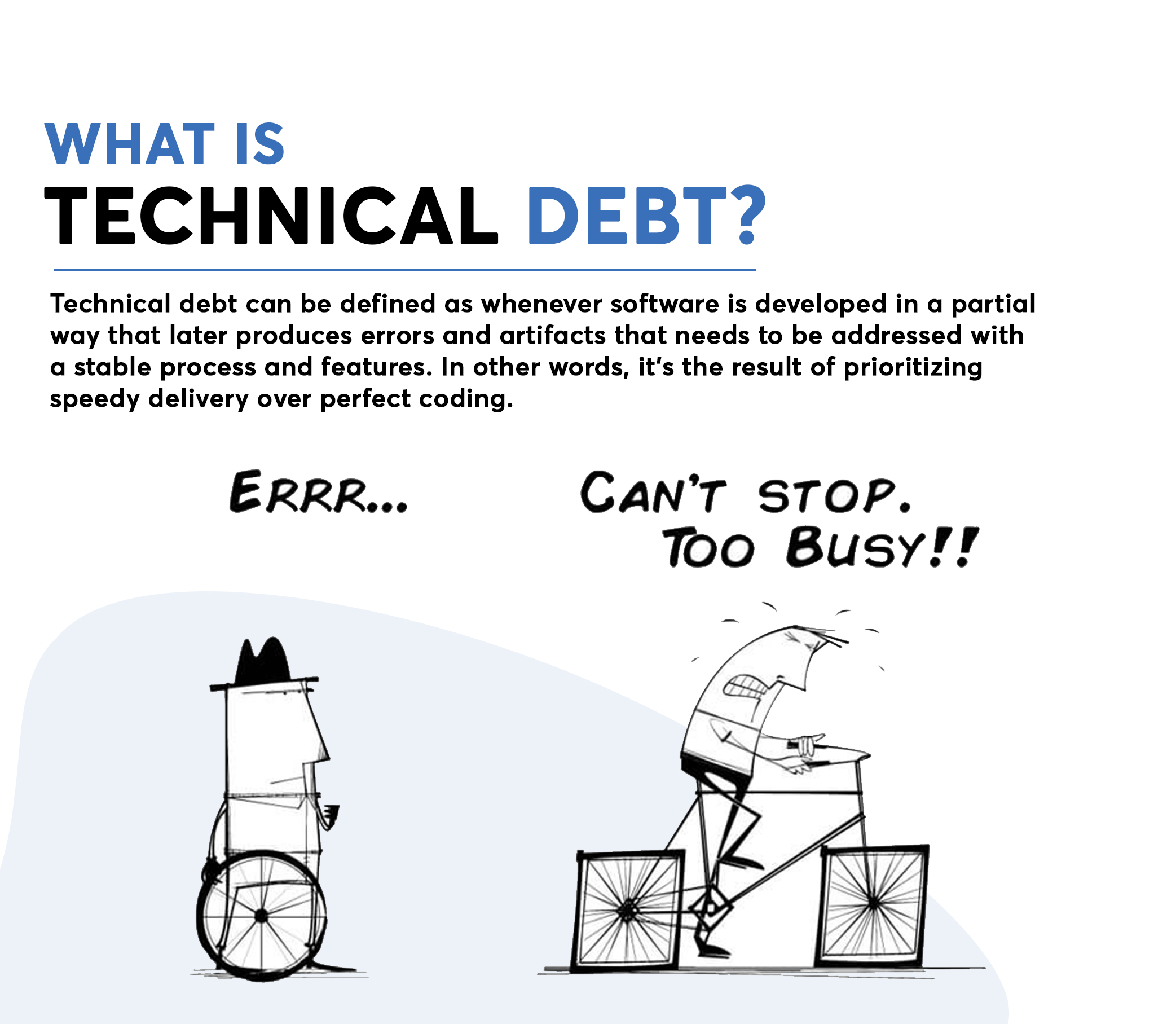 What is technical debt?
What is technical debt?
Ever wonder what happens when a problem is not solved but ignored? The problem is buried deep down and overlooked completely. This issue is not an issue until it becomes one, creating more difficulty on a large scale.
Such is the case with technical debt. It is a concept in software development where developers focus on creating an application with limited features in a short time that would later need restructuring. It occurs mainly when shortcuts are taken to develop a feature or a product. Technical debt can be defined as whenever software is developed in a partial way that later produces errors and artifacts that needs to be addressed with a stable process and features. In other words, it’s the result of prioritizing speedy delivery over perfect coding.
 How does Technical debt occur?
How does Technical debt occur?
Technical debt occurs because it takes much time to develop specific features and add modifications, thus delaying its launch in the market. The developer needs to go back and fix the glitches or bugs, which is a tedious task. Often, different developers work on the bugs from the ones who originally built the software, which makes it even more challenging to address the problem.
Developers coming up with a new product starts with a prototype application. Programmers built the software in a shorter time frame with limited features to test it in the market. Customers with limited access are sometimes also known as beta testers. If the testing phase pays off, the developer would then move on to the next stage of actually producing the software on a large scale. The production would include customization, detailing add-ons features, smoother interface, notifications, etc.
Sometimes features are not added to the apps in the beta phase because of quick production and market rivalry. Hence the developer produces the app in a suboptimal way, thus making maintenance difficult. The product needs to address its shortcomings at some point for it to function smoothly. Though from a customer and business perspective, it seems to work very well.
But from the developer’s point of view, it has its shortcomings that need to be addressed. If these shortcomings are not dealt with, it could cause havoc and crashes in the application at a later stage. The app could not function properly and may even have a lot of glitches, resulting in a (technical) debt weighing on the developer team. This technical debt keeps on piling up unless it is addressed.
Analysis of technical debt
‘Code smells’ is a term for poorly implemented code causing disturbance to the software development process. This leads to reducing the quality of the code and therefore increasing technical debt when multiple programmers are working on separate parts of the same programs leads to duplication of code all over the application, thus leading to code smells.
Code complexity
It refers to the number of systems defining a software application and the number of operations amongst them. Developing code in a short time frame due to the demand leads to overly complex unstructured code.
Lack of documentation
When the documentation is outdated and has errors, it isn’t easy to understand the components, making modifications to the code complex.
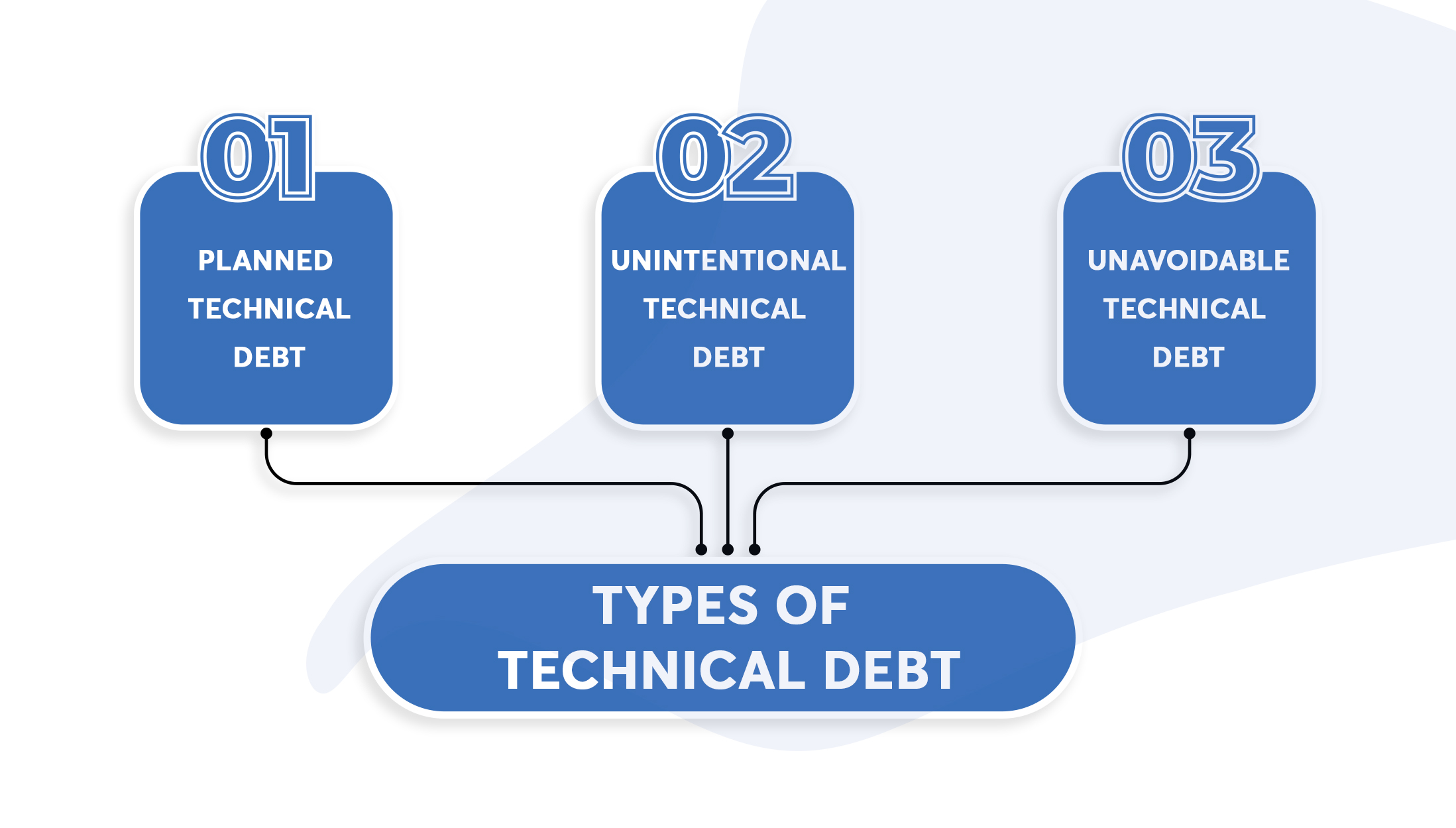 Types of technical debt
Types of technical debt
Planned technical debt
This type of debt is intentionally created to push the product up front in the market ahead of the rival competition. Generating debt on purpose will have consequences such as reliability of the product, the future development and difficulty in launching new features in the future. A company launching a product in the market at times skips certain aspects like testing the project after and before the release hence contributing to technical debt.
Unintentional technical debt
This refers to lousy coding and not being compatible with enough designed components in the application. Reviews, training, and static analysis are essential, along with good coding skills to prevent unintentional technical debt.
Unavoidable technical debt
This happens when the situation is not in control of the development team and organization as a whole. It usually occurs when there’s a new technology implementation in the industry. Such as upgrade of third party systems, introduction to new languages and new devices
Hence at times to avoid technical debt, developers need to make their codebase a little less complex. In case new implementations are required. It will further save the cost of rework and redevelopment.
How to prevent technical debt?
It is essential to educate developers that technical debt is a problem. It is vital to realize that a code built differently by a developer is far more difficult to modify later on with a different set of teams. It would take far more time to unravel things and add new features. At times too many shortcuts taken in the development will end up in complex fixes and lengthy procedures.
Sometimes timelines are essential to get products in time, but developers are pushed hard by managers or business executives. The constant pressure leads to developing an app that could have been made the right way to function abnormally. Hence creating the app the right way could prevent the technical debt from forming in the first place.
All systems have some amount of technical debt. Not everything is always perfect. Most of the time, developers will have to deal with technical debt.
How to fix technical debt?
It is important to allocate time to fix the glitches and debt. If shortcuts are taken to develop, which results in many drawbacks, it needs to be cleaned up. The fixing of technical debt takes a lot of time, especially when the software has been created long back, thus piling up more and more technical debt. Hence it’s crucial to have as little technical debt as possible. A short amount of technical debt is acceptable, but things start to get frustrating for a developer as soon as it piles up.
The other way to fix technical debt is to rebuild the system. The amount of time involved in pairing and rebuilding the system is enormous. It is also a very time-consuming task which again consists of a lot of research and skills. Therefore it is crucial to address technical debt in the first place when the time is allocated to fix the malfunction.
It will be challenging to add new features and modifications if not dealt with technical debt, thus slowing down the software and crippling the entire system. Eventually, making the application lag and malfunction.
Can it be helpful or prudent ?
There are conflicting aspects of technical debt. Startups, in particular, feel the need to swim or sink that forces them to make a technical debt over a delayed launch. Technical debt is not all that bad; most companies do have little portions of it. Software teams believe in not having any debt and a transparent, clean sheet. Business executives tend to have an open mind towards technical debt as it gives them an edge over their competitors.
In general technical debt is like financial debt. It is not a problem until it becomes one. With careful management of time and resources, technical debt can be reduced to a minimum. That way, developers may focus their time more on other productive aspects of software applications.
Chapter 247 offers a variety of business models in terms of product development. Our team is an eclectic mix of coders, project managers, developers, marketing professionals and technical trainers. We have a track record of successfully managing overseas projects within timelines. If you are dreading technical debt, we should talk.